Profile of the oral microbiota from preconception to the third trimester of pregnancy and its association with oral hygiene practices
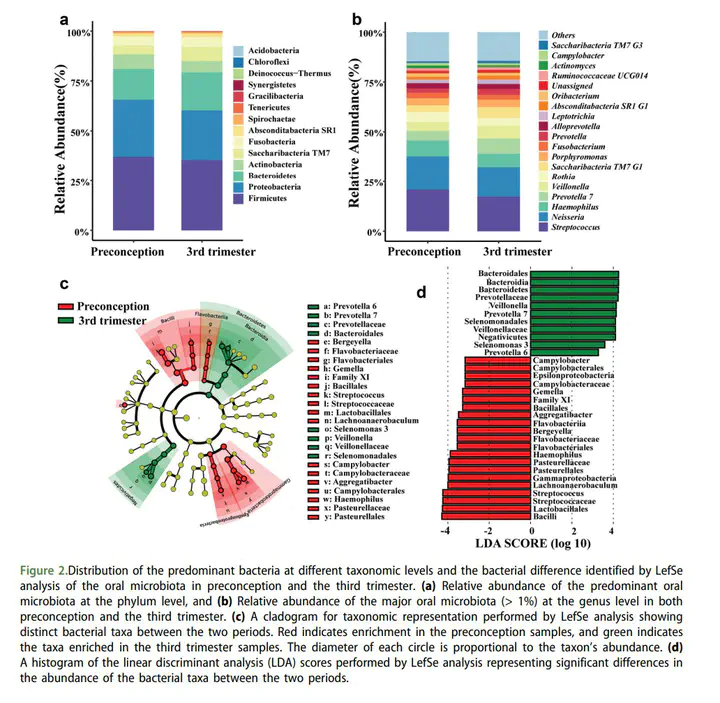 Image credit: Unsplash
Image credit: UnsplashAbstract
The oral microbiota plays vital roles in both oral and systemic health, but limited studies have explored the transition of the female oral microbiota from preconception to pregnancy along with pronounced hormonal fluctuations. To characterize the oral microbiota among women in preconception and pregnancy through a prospective study and to explore the associations between the oral microbiota and oral hygiene practices. A total of 202 unstimulated saliva samples were collected from 101 women in both preconception and late pregnancy. The oral microbiota was analyzed using 16S rRNA gene sequencing. The Ace and phylogenetic diversity (PD) index were significantly lower in the third trimester than preconception. The pathogenic taxa Prevotella and Atopobium parvulum were significantly higher during late pregnancy than preconception. Women with overall better oral.